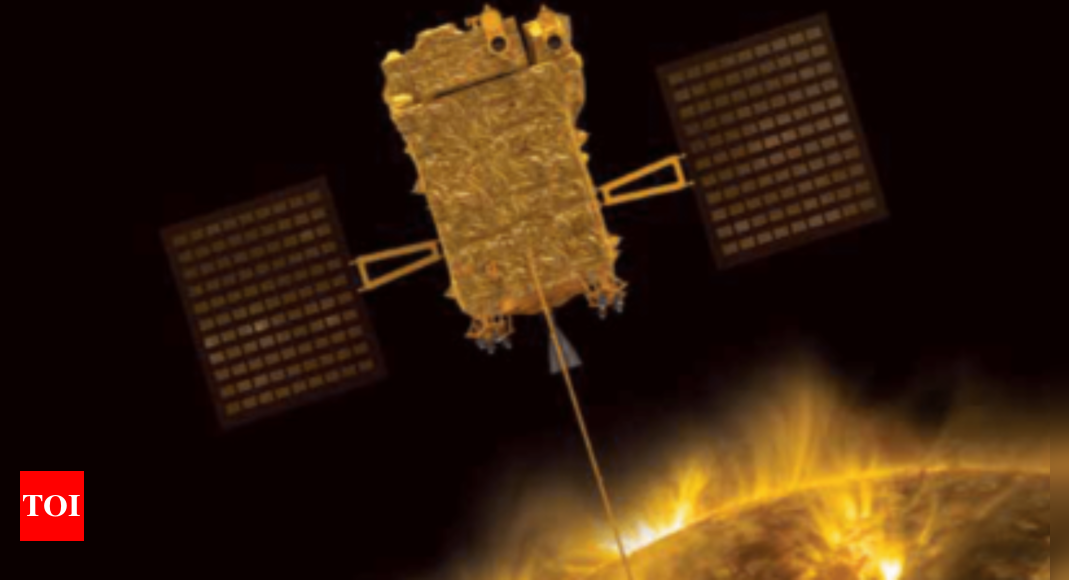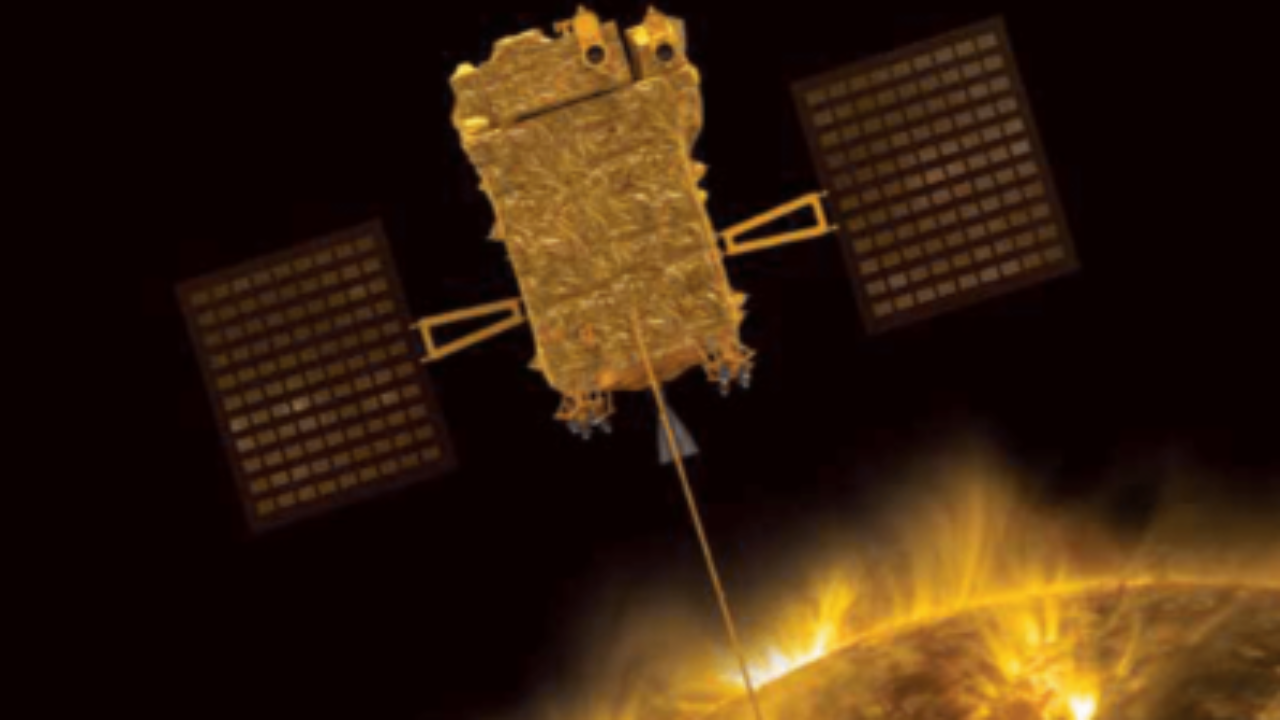
BENGALURU: India’s first solar space observatory, Aditya-L1, which has travelled beyond a distance of 9.2 lakh kilometres from Earth, successfully escaping the sphere of Earth’s influence, is heading towards a location 1.5 million-km away from Earth, with Isro keeping a close eye on its journey.
However, reaching that destination isn’t the only challenge Adityafaces. Staying there is also tricky.To ensure it gets to its destination and stays safely in orbit, Isro needs to know exactly where their spacecraft “was, is and will be”.
When one large mass orbits another, their gravitational forces and orbital motion interact to create five equilibrium points where a spacecraft can operate for a prolonged period of time without having to use a lot of fuel. These locations are known as Lagrange points. Aditya-L1’s final destination will be one of the five Lagrange points in the Sun-Earth system.
Also known as libration points, Lagrange points are unique locations in space where the gravitational force of two massive bodies (like Sun and Earth) precisely equals the centripetal force required for a small object (like spacecraft) to move with them.
L1, where Aditya will go, is particularly significant because it is situated between the two primaries (Sun and Earth), making it an ideal location for spacecrafts because they allow continuous observation of primary bodies, continuous communication with earth and an unobstructed view of celestial bodies.
These orbits are well-suited for scientific missions like Aditya which will act like a solar observatory around L1 and communicate to Earth.
The challenge
According to the European Space Agency (ESA), L1 is one of the ‘unstable’ Lagrange points and keeping a spacecraft exactly at the L1 point is practically impossible.
“Instead, spacecraft enter orbit around L1 as if the Lagrange point were an ‘invisible planet’. Even so, due to the instability of this orbit, small trajectory errors will grow quickly. As a result, spacecraft must perform ‘station keeping’ manoeuvres roughly once a month to keep them in the correct orbit.”
Somanath said while L1 is an unstable point, the instability is very mild and spread over a long period of time making it still the best place to be for a spacecraft. “L3 and L4 are much more difficult, for instance.”
“…That said, if we aren’t careful with regard to orbit determination then the spacecraft can diverge. While it can be brought back, the fuel penalty will be higher,” he said.
L1 & software
Theoretically, L1 is a constant point. It is a geometrical point that one gets when one connects the Moon, Sun and Earth.
Although L1 is theoretically between two objects, when it gets influenced by other bodies, the Moon for instance, it becomes a multi-body sphere. And depending on the movement of these bodies, there are changes Isro will need to account for with time.
“The halo orbit Aditya-L1 will be in is a vague orbit. It’s not like rotating around a single point. It is rotating around a vast area that is a three-dimensional orbit. Therefore, the need was for a multi-body computational programme to find out the trajectory of these bodies and the spacecraft. For this, Isro has designed and developed new orbit determination software for Aditya-L1,” Somanath said.
However, reaching that destination isn’t the only challenge Adityafaces. Staying there is also tricky.To ensure it gets to its destination and stays safely in orbit, Isro needs to know exactly where their spacecraft “was, is and will be”.
This tracking process, called ‘orbit determination,’ involves using mathematical formulas and specially developed software by Isro’s UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), Isro chairman S Somanath told TOI.
When one large mass orbits another, their gravitational forces and orbital motion interact to create five equilibrium points where a spacecraft can operate for a prolonged period of time without having to use a lot of fuel. These locations are known as Lagrange points. Aditya-L1’s final destination will be one of the five Lagrange points in the Sun-Earth system.
Also known as libration points, Lagrange points are unique locations in space where the gravitational force of two massive bodies (like Sun and Earth) precisely equals the centripetal force required for a small object (like spacecraft) to move with them.
Aditya-L1 solar mission captures stunning Earth and Moon images, completes manoeuver
L1, where Aditya will go, is particularly significant because it is situated between the two primaries (Sun and Earth), making it an ideal location for spacecrafts because they allow continuous observation of primary bodies, continuous communication with earth and an unobstructed view of celestial bodies.
These orbits are well-suited for scientific missions like Aditya which will act like a solar observatory around L1 and communicate to Earth.
The challenge
According to the European Space Agency (ESA), L1 is one of the ‘unstable’ Lagrange points and keeping a spacecraft exactly at the L1 point is practically impossible.
“Instead, spacecraft enter orbit around L1 as if the Lagrange point were an ‘invisible planet’. Even so, due to the instability of this orbit, small trajectory errors will grow quickly. As a result, spacecraft must perform ‘station keeping’ manoeuvres roughly once a month to keep them in the correct orbit.”
Somanath said while L1 is an unstable point, the instability is very mild and spread over a long period of time making it still the best place to be for a spacecraft. “L3 and L4 are much more difficult, for instance.”
“…That said, if we aren’t careful with regard to orbit determination then the spacecraft can diverge. While it can be brought back, the fuel penalty will be higher,” he said.
L1 & software
Theoretically, L1 is a constant point. It is a geometrical point that one gets when one connects the Moon, Sun and Earth.
Although L1 is theoretically between two objects, when it gets influenced by other bodies, the Moon for instance, it becomes a multi-body sphere. And depending on the movement of these bodies, there are changes Isro will need to account for with time.
“The halo orbit Aditya-L1 will be in is a vague orbit. It’s not like rotating around a single point. It is rotating around a vast area that is a three-dimensional orbit. Therefore, the need was for a multi-body computational programme to find out the trajectory of these bodies and the spacecraft. For this, Isro has designed and developed new orbit determination software for Aditya-L1,” Somanath said.
Source link